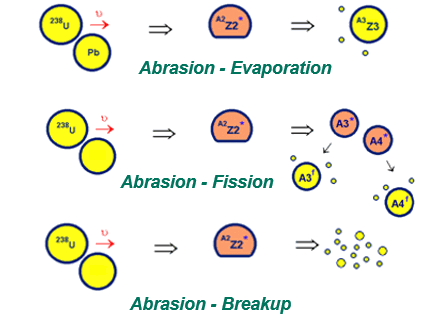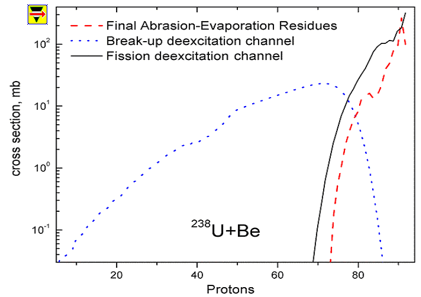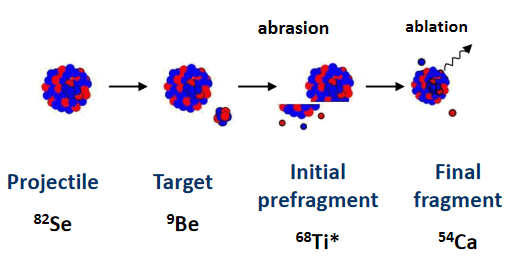
1. Introduction: Heavy Ions reactions at intermediate and high energies 2. Geometrical Abrasion-Ablation model 3. Ablation stage (Evaporation cascade) 4. Abrasion-Ablation & Evaporation calculator Prefragment Excitation energy Selection of Abrasion-Ablation model to calculate cross sections Plotting Abrasion-Ablation cross sections Mass model choice 6. Abrasion-Ablation vs. Experimental data Minimization 7. Abrasion-Ablation model development in LISE++ 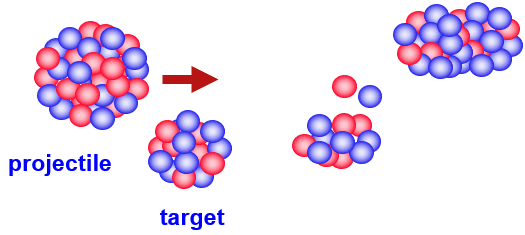 1. Introduction: Heavy Ions reactions at intermediate and high energies
2. Geometrical Abrasion-Ablation model Geometrical LISE++ Abrasion-Ablation Model is a simple theory of fragmentation based upon a two-step model [Wil87]. The abrasion process accounts for removal of nuclear matter in the overlap region of the colliding ions. An average transmission factor is used for the projectile and target nuclei at a given impact parameter to account for the finite mean-free path in nuclear matter. The ions are treated otherwise on a geometrical basis assuming uniform spheres. The surface distortion excitation energy of the projectile prefragment following abrasion of nucleons is calculated from the clean-cut abrasion formalism [Gos77]. [Gos77] J.Gosset et al., Phys.Rev. C16 (1977) 629.[Wil87] J.W.Wilson, L.W.Towsend, F.F.Badavi, NIM B18 (1987) 225-231. Currently the code contains four methods to calculate a prefragment excitation energy (See the dialog below). Menu ➝ Physics Models ➝ Excitation Energy of Prefragment 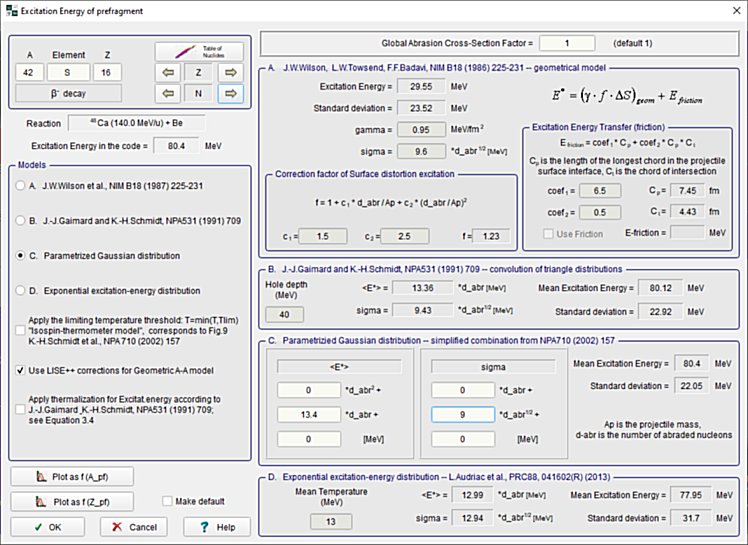 Fig. The Prefragment excitation energy dialog (Click to zoom). 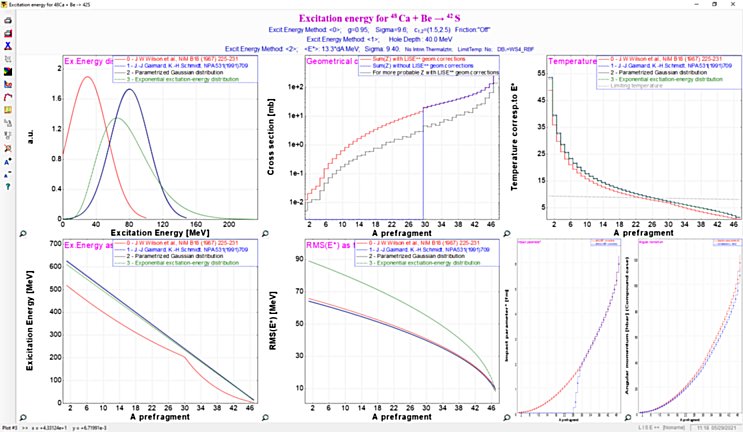 Fig. The Prefragment excitation energy plots (Click to zoom). 3. : Ablation stage (Evaporation cascade) The Ablation step is based on the fusion-evaporation model LisFus [Tar03] for fast analytical calculations of fusion residues cross sections, where the evaporation stage is treated in a macroscopic way on the basis of a master equation which leads to diffusion equations as proposed by Campi and Hűfner [Cam81], and reexamined lately by Gaimard and Schmidt [Gai91]. Level densities and decay widths are taken from the statistical analysis of Iljinov et al. [Ilj92]. The LISE evaporation model works with probability distributions as function of excitation energy taking into account initially eight possible parent and daughter channels (n, 2n, p, 2p, d, t, 3He, a), and fission and breakup de-excitation channels implemented later [Tar08f]. Analytical solution of the evaporation cascade was performed with the transport integral theory [Baz94] providing fast calculations, that allows to calculate the cross-section for nuclei far from stability which are not accessible with Monte Carlo technique. [Baz94] D. Bazin, B. Sherrill, Phys. Rev. E 50 (1994) 4017.[Gai91] J.-J.Gaimard, K.-H.Schmidt, Nucl.Phys. A531 (1991) 709-745. [Ilj92] A.S. Iljinov et al., Nucl. Phys. A543 (1992) 517. [Tar03] O.B. Tarasov, D. Bazin, NIM B 204 (2003) 174-178. [Tar08f] O.B. Tarasov, A.C.C.Villari, NIM B 266 (2008) 4670-4673. Menu ➝ Physics Models ➝ Prefragment Search & Evaporation options  Fig. Prefragment Search & Evaporation options dialog (Click to zoom). 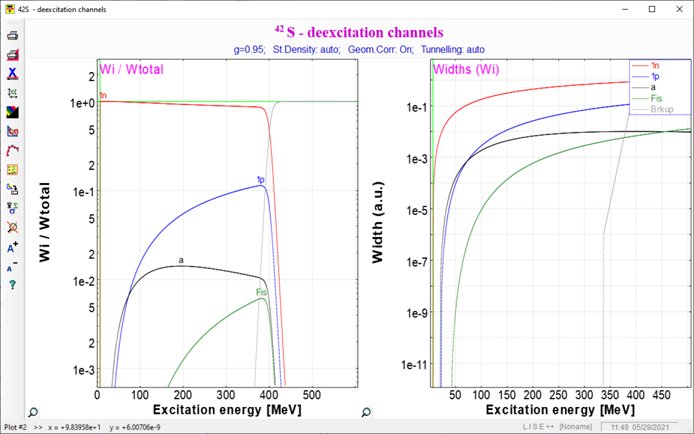 Fig. De-excitation channels plot (Click to zoom). 4. Abrasion-Ablation / Evaporation calculator The "Evaporation calculator" is available in the Calculations menu or via the icon
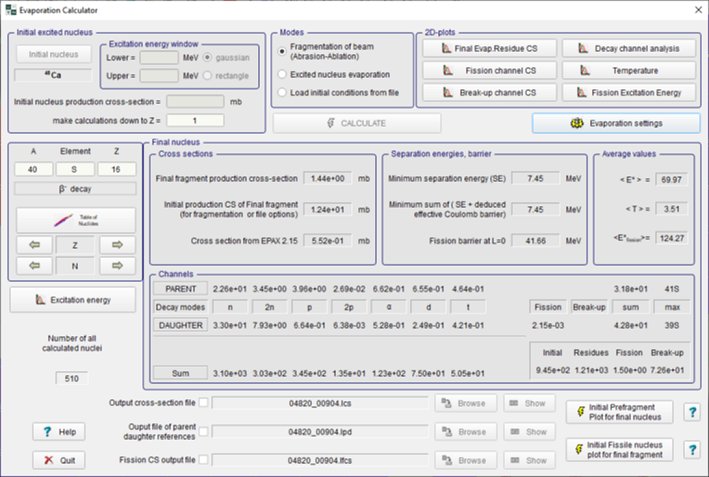 Fig.4.1. The Evapoaration dialog in action (Click to zoom). 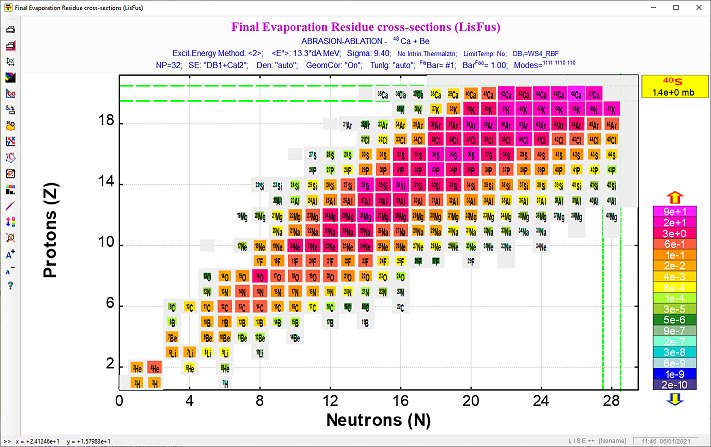 Fig.4.2. Two-dimensional plot of calculated cross-sections. The data is represented by rectangles centered at N (neutrons) and Z (protons), where the cross-section value depends on color and size of the rectangle. The user can change the display modes of rectangles, and also change the scale (Click to zoom). 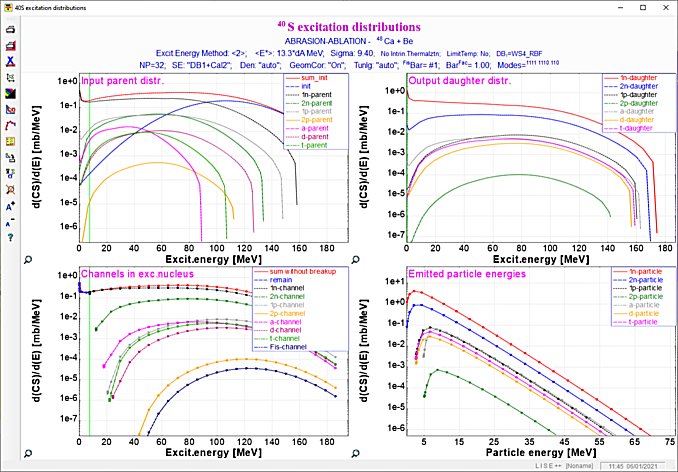 Fig.4.3. Excitation functions of 40Ca produced in reaction of the 48Ca beam with a Be-target. (Click to zoom). 06/02/2001 v.4.18 Evaporation Calculator ⊙ Evaporation cascade ⊙ Prefragment Excitation energy ⊙ Selection of Abrasion-Ablation model to calculate cross sections Menu ➝ Physics Models ➝ Production Mechanism ➝  ⊙ Plotting Abrasion-Ablation cross sections Before plotting cross-sections with preliminary it is necessary to check the "Show Abasion-Ablation in X-section plots" box in the Preference dialog:  ⊙ Mass model choice Menu ➝ Physics Models ➝ Production Mechanism ➝ "Database: Masses, Isomers" tab  6. Abrasion-Ablation vs. Experimental data Menu ➝ Utilities ➝ Reaction utilities ➝ 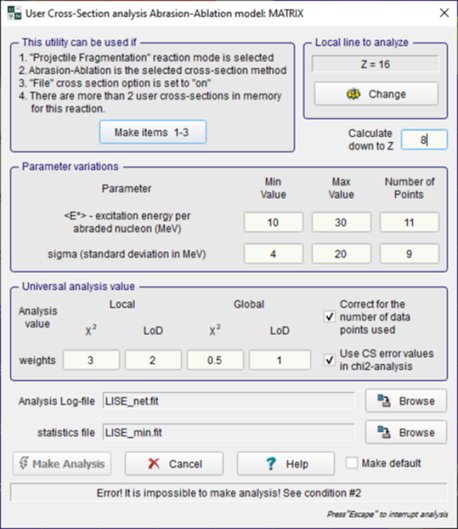 Fig. Dialog of User cross-section analysis using Abrasion-Ablation model (Matrix method) 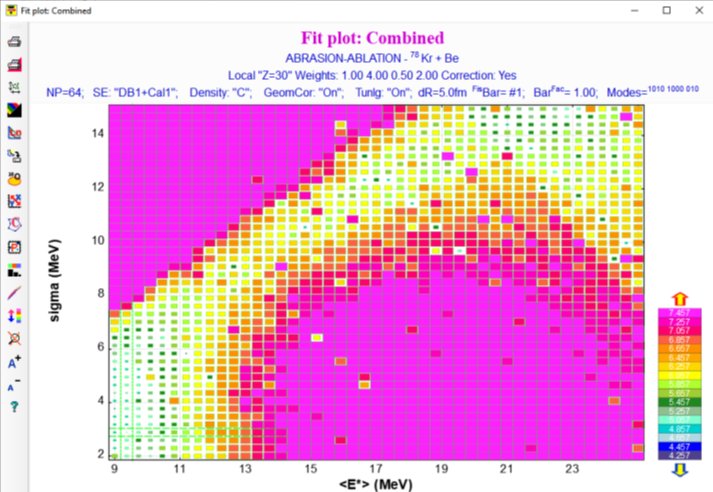 Fig. Final plot combined on four plots (Local-chi2, Local-LoD, Global-chi2, Global-LoD) based on user weights. Menu ➝ Utilities ➝ Reaction utilities ➝ The new minimization utility recently developed in the LISE code
allows to deduce Abrasion-Ablation model parameters from comparison of
AA-calculation results with experimental cross-sections with selection
one from 28 mass models distributed with the LISE++ suite. The utility
is based on the [LevMar] M.I.A. Lourakis, levmar: Levenberg–Marquardt nonlinear least squares algorithms in C/C++, http://www.ics.forth.gr/lourakis/levmar/, 2004. 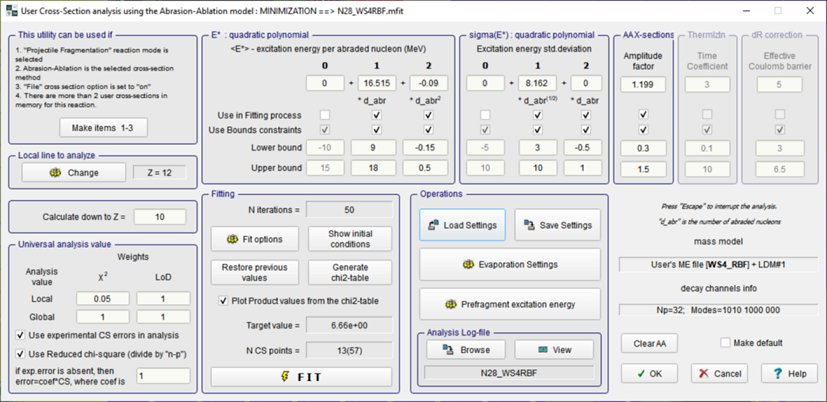 Fig. Dialog of User cross-section analysis using Abrasion-Ablation model (Minimization method) (Click to zoom). 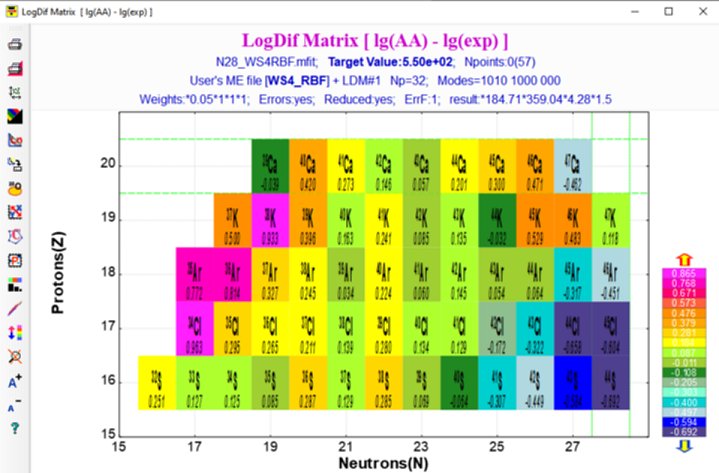 Fig. Plot of logarithm ratios of Abrasion-Ablation calculations and experimental values. 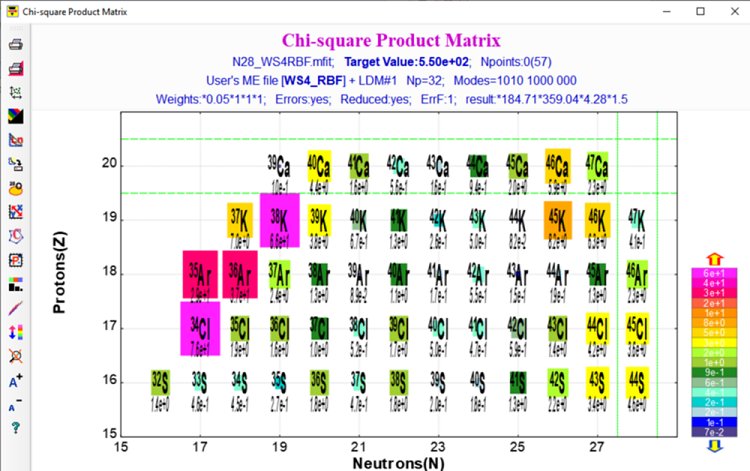 Fig. Plot of chi-square values. 7. Abrasion-Ablation model development in LISE++
06/02/2001 v.4.18 Abrasion-Ablation v.1.0 8. LISE AA model next development plans
⋅ benchmarks of the "Distribtuion" method, ⋅ using more sophisticated event gates , ⋅ application of angular momentum |